Browse Source
add more converted blog posts.. This should be all of them...
they still need to be proofed to make sure they got fully converted.main
11 changed files with 793 additions and 0 deletions
Split View
Diff Options
-
+124 -0content/2015/07/installing-and-running-netbsd-and.html
-
+100 -0content/2017/09/adventures-in-autobahnwamp-security.html
-
+3 -0content/2017/meta.yaml
-
+80 -0content/2018/03/unusable-insecurity.html
-
+163 -0content/2018/07/making-freebsd-magnet-links.html
-
+118 -0content/2018/10/crash-dumps-do-i-submit-them.html
-
+93 -0content/2018/10/tls-client-authentication-leaks-user.html
-
+3 -0content/2018/meta.yaml
-
+106 -0content/2019/04/using-signal-on-server.html
-
+3 -0content/2019/meta.yaml
-
BINcontent/media/images/tls.packet.capture.screenshot.png
+ 124
- 0
content/2015/07/installing-and-running-netbsd-and.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,124 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: Installing and running NetBSD and OpenBSD under bhyve | |||
| description: > | |||
| Installing and running NetBSD and OpenBSD under bhyve | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2015-07-28' | |||
| time: 8:37 PM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - NetBSD | |||
| - OpenBSD | |||
| - byhve | |||
| - FreeBSD | |||
| --- | |||
| These instructions assume that you have downloaded the install ISO from | |||
| the respective sources. These were doing with specific versions, and | |||
| there may be minor changes with older and newer versions. | |||
| These instructions could possibly be more simple, such as not using | |||
| separate device maps for `grub-bhyve`. These were testing on a month | |||
| old HEAD. | |||
| There are other guides that cover most of this, and probably in more | |||
| detail. The issue that I had was the exact commands to grub to load | |||
| kernels was not well documented. Both of the images boot and are able | |||
| to get DHCP leases and pass basic traffic. | |||
| Hope this helps others! | |||
| ## NetBSD | |||
| 1. Install `grub2-bhyve`: | |||
| ``` | |||
| pkg install grub2-bhyve | |||
| ``` | |||
| 2. Create a file called `instdev.map` containing: | |||
| ``` | |||
| (cd0) NetBSD-6.1.5-amd64.iso | |||
| (hd1) netbsd.img | |||
| ``` | |||
| 3. Create the file `netbsd.img` with the correct size: | |||
| ``` | |||
| truncate -s 3g netbsd.img | |||
| ``` | |||
| 4. Run the following commands (or put into a script file) under `sh`: | |||
| ``` | |||
| MEM=512M | |||
| VM=nbsd615 | |||
| bhyvectl --destroy --vm=$VM | |||
| grub-bhyve -r cd0 -M $MEM -m instdev.map $VM <<EOF | |||
| knetbsd -h -r cd0a | |||
| (cd0)/netbsdboot | |||
| EOF | |||
| bhyve -A -H -P -s 0:0,hostbridge -s 1:0,lpc \ | |||
| -s 2:0,virtio-net,tap3 -s 3:0,virtio-blk,./netbsd.img \ | |||
| -s 4:0,ahci-cd,./NetBSD-6.1.5-amd64.iso \ | |||
| -l com1,stdio -c 2 -m $MEM $VM | |||
| ``` | |||
| 5. This will run the installer, complete the installation. | |||
| 6. Create a file called `dev.map` containing: | |||
| ``` | |||
| (hd1) netbsd.img | |||
| ``` | |||
| 7. Now in the future, to run NetBSD from the image, run the following commands: | |||
| ``` | |||
| MEM=512M | |||
| VM=nbsd615 | |||
| bhyvectl --destroy --vm=$VM | |||
| grub-bhyve -r cd0 -M $MEM -m dev.map $VM <<EOF | |||
| knetbsd -h -r ld0a | |||
| (hd1,msdos1)/netbsdboot | |||
| EOF | |||
| bhyve -A -H -P -s 0:0,hostbridge -s 1:0,lpc \ | |||
| -s 2:0,virtio-net,tap3 -s 3:0,virtio-blk,./netbsd.img \ | |||
| -l com1,stdio -c 2 -m $MEM $VM | |||
| ``` | |||
| 8. Profit! | |||
| ## OpenBSD | |||
| 1. Install `grub2-bhyve`: | |||
| ``` | |||
| pkg install grub2-bhyve | |||
| ``` | |||
| 2. Create a file called `instdev.map` containing: | |||
| ``` | |||
| (cd0) install57.iso | |||
| (hd1) openbsd.img | |||
| ``` | |||
| 3. Create the file `openbsd.img` with the correct size: | |||
| ``` | |||
| truncate -s 3g openbsd.img | |||
| ``` | |||
| 4. Run the following commands (or put into a script file) under `sh`: | |||
| ``` | |||
| MEM=512M | |||
| VM=obsd57 | |||
| bhyvectl --destroy --vm=$VM | |||
| grub-bhyve -r cd0 -M $MEM -m instdev.map $VM <<EOF | |||
| kopenbsd -h com0 | |||
| (cd0)/5.7/amd64/bsd.rdboot | |||
| EOF | |||
| bhyve -A -H -P -s 0:0,hostbridge -s 1:0,lpc \ | |||
| -s 2:0,virtio-net,tap3 -s 3:0,virtio-blk,./openbsd.img \ | |||
| -s 4:0,ahci-cd,./install57.iso \ | |||
| -l com1,stdio -c 2 -m $MEM $VM | |||
| 5. This will run the installer, complete the installation. | |||
| 6. Create a file called `dev.map` containing: | |||
| ``` | |||
| (hd1) netbsd.img | |||
| ``` | |||
| 7. Now in the future, to run OpenBSD from the image, run the following commands: | |||
| ``` | |||
| MEM=512M | |||
| VM=obsd57 | |||
| bhyvectl --destroy --vm=$VM | |||
| grub-bhyve -r hd1 -M $MEM -m dev.map $VM <<EOF | |||
| kopenbsd -h com0 -r sd0a | |||
| (hd1,openbsd1)/bsdboot | |||
| EOF | |||
| bhyve -A -H -P -s 0:0,hostbridge -s 1:0,lpc \ | |||
| -s 2:0,virtio-net,tap3 -s 3:0,virtio-blk,./openbsd.img \ | |||
| -s 4:0,ahci-cd,./install57.iso \ | |||
| -l com1,stdio -c 2 -m $MEM $VM | |||
| 8. Profit! | |||
+ 100
- 0
content/2017/09/adventures-in-autobahnwamp-security.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,100 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: Adventures in Autobahn/WAMP Security | |||
| description: > | |||
| Adventures in Autobahn/WAMP Security | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2017-09-17' | |||
| time: 12:21 PM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - web | |||
| - WAMP | |||
| - security | |||
| --- | |||
| ## Or how security continues to suck because: It's Hard and Someone Else's Problem™ | |||
| For a personal project, I've decided to use WAMP to move some events and | |||
| messages around between different components. I decided on the AutoBahn | |||
| libraries and Crossbar.io as the router. I was already somewhat familiar | |||
| w/ AutoBahn from previous work, and the Crossbar.io router seems to just | |||
| work. As a security person, I decided to evaluate how to make things as | |||
| secure as possible. | |||
| First off, | |||
| [my projects must be both authenticated and encrypted](https://twitter.com/encthenet/status/881596129573347328). | |||
| WAMP does not appear to have it's own encryption layer, but it does have | |||
| it's own authentication layer. You really don't want to have to trust | |||
| two different authentication layers<label for="sn-encauth" | |||
| class="margin-toggle sidenote-number"></label><input type="checkbox" | |||
| id="sn-encauth" class="margin-toggle"/><span class="sidenote" | |||
| id="sn-encauth">The encryption layer must be authenticated, otherwise | |||
| any attacker could MiTM the connection. Most uses of TLS make use of | |||
| the CA system for authentication (which has serious issues in trust), | |||
| and most web apps add their own authentication layer on top of it (not | |||
| using Basic Auth, or other scheme). The issues w/ this is that if there | |||
| is no binding between the two layers, the lower layer (application | |||
| layer) cannot be sure that the upper layer has not been compromised.</span>, | |||
| so being able to use | |||
| [TLS Channel Bindings](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5929) would be an | |||
| improvement. This would ensure that a strong authentication method in | |||
| WAMP would ensure that the channel is properly encrypted. I | |||
| [received confirmation](https://twitter.com/crossbario/status/904690145907142656) | |||
| from the Crossbar.io team that it was present. | |||
| Autobahn and Crossbar.io supports a number of | |||
| [different authentication schemes](https://crossbar.io/docs/Authentication/). | |||
| As I plan on putting this behind a reverse proxy (which I realize will | |||
| have it's own issues w/ channel binding), I wanted the strongest security | |||
| binding between my client and the server (and I'm a glutton for punishment | |||
| for using unproven tech). The only one that satisfies this requirement | |||
| is WAMP-Cryptosign. | |||
| After I got basic functionality working to make sure things would be | |||
| workable w/ this framework, I decided to start working on the | |||
| authentication piece. First problem I ran into was that the AutoBahn|JS | |||
| library does not support TLS channel binding. There is a good read the | |||
| library doesn't support it, and it's for a very bad reason. There is | |||
| no support in the browser [WebSocket API](https://www.w3.org/TR/websockets/) | |||
| to query the channel binding information necessary. The fact that | |||
| WebSockets was standardized after Channel bindings were demonstrates that | |||
| the people involved in standardizing the web do not take security | |||
| seriously. As usual, they assume that security is not their problem and | |||
| leaves it up to someone else to solve (or at another layer). | |||
| Disappointed that I wouldn't be able to use channel bindings w/ the web | |||
| client for this project (I still had the crappy CA authentication of TLS, | |||
| so not all was lost), I moved forward w/ CryptoSign. As has been | |||
| demonstrated many times, the only way to get security baked in, is to | |||
| make it as easy as possible to use. I've been long familiar w/ | |||
| [Crypto Box](https://nacl.cr.yp.to/box.html) by djb (and used by the | |||
| Autobahn libraries), and also the [noise protocol](http://noiseprotocol.org/) | |||
| (which my friend Trevor created). Both of these have goals of making | |||
| it simple to let developers include security in their projects and not | |||
| mess it up, resulting in a broken system. As currently implemented, | |||
| Autobahn's CryptoSign is most definitely not easy to use. | |||
| Though the documentation is decent, some examples are not present | |||
| (`client_ssh_key.py` for example from | |||
| [WAMP-cryptosign Static Authentication](https://github.com/crossbario/crossbar-examples/tree/master/authentication/cryptosign/static)). | |||
| The | |||
| [ApplicationRunner](http://autobahn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/wamp/programming.html#running-components) | |||
| helper class does not document how to make use of authentication. Though | |||
| the static authentication page has examples, they make you write quite | |||
| a bit of boiler plate. | |||
| Then even once you do that, you find out that the code doesn't even work | |||
| on Python 2.7 and have to | |||
| [fix it](https://github.com/crossbario/autobahn-python/pull/901) for | |||
| them. Hopefully the pull request (PR) will not be ignored because of the | |||
| failing CI tests, because the current CI tests are problems with their | |||
| CI environment, and not the PR. For CI checks like this, it should only | |||
| ding your PR on checks that are newly failing, and ignore any checks that | |||
| were previously failing. This isn't the first project that their CI | |||
| environment was broken. | |||
| Even w/ the fixes in place, there is no documented method of extracting | |||
| a public key from a generated ssh key. I will be adding a method to | |||
| print this out. | |||
| If I (who knows cryptography decently) have to fix and spend hours making | |||
| this work, it's no wonder than everyone things that strong cryptography | |||
| is hard. It is hard, but it shouldn't be. | |||
+ 3
- 0
content/2017/meta.yaml
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ | |||
| extends: blog.j2 | |||
| default_block: post | |||
| listable: true | |||
+ 80
- 0
content/2018/03/unusable-insecurity.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,80 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: Unusable Insecurity | |||
| description: > | |||
| Unusable Insecurity | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2018-03-16' | |||
| time: 1:40 PM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - security | |||
| --- | |||
| Many people claim that security is hard, and in many cases it is hard, | |||
| but that isn't an excuse to make it harder than it needs to be. There | |||
| are many layers to security, but adding extra layers, or making security | |||
| controls inscrutable is a great way to ensure insecurity. Security needs | |||
| to be simple and straightforward to configure, and easy to understand. | |||
| There may be knobs for advanced users, but defaults need to be simple and correct. | |||
| I recently looked at using S3 as a shared store for some data. I was | |||
| using the account New Context created for me that had limited AWS | |||
| permissions. Creating the S3 bucket was simple enough, and making it | |||
| not-public was too, but then I wanted to create a user/API key that only | |||
| had access to the S3 bucket. Per Amazon | |||
| [IAM Best Practices](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html), | |||
| you should not share your account, but create new users for access. It | |||
| turns out that I did not have the CreateUser permission. I involved a | |||
| co-worker who did have permissions to create the user. Adding another | |||
| person to the task makes things more complex through communication and | |||
| their availability to work on it instead of their normal work. | |||
| As part of creating a user, you have to figure out what the Policy that | |||
| you need to assign to the user. Amazon provides some | |||
| [Bucket Policy Examples](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/example-bucket-policies.html), | |||
| but none of them is a simple policy on granting read and write permissions | |||
| to the bucket. There is an | |||
| [Amazon Policy Generator](https://awspolicygen.s3.amazonaws.com/policygen.html) | |||
| for helping you to create the policies, but it doesn't allow you to | |||
| select buckets from your account (to simplify ARN [Amazon Resource Name] | |||
| selection), and there are almost 70 actions provided in the selector. | |||
| After some brief reading, I settled on a simple policy that I thought | |||
| would allow the new user proper access: 4 permissions: PutObjects, | |||
| GetObjects, ListObjects and RestoreObjects. | |||
| My co-worker created the user and applied the policy, but then I got an | |||
| error handle code. Amazon does not provide an interface for turning on | |||
| logging and/or querying why a request failed. Despite the error handle, | |||
| I had ZERO insight into why the request failed. I could have involved | |||
| AWS support, but now that would add yet another party in attempting to | |||
| properly configure S3. | |||
| At this stage, I decided to give up, as I had already spent a few hours | |||
| of my time, some of my co-worker's time, and a couple weeks due to | |||
| various delays due to availability and other work. In this case, storing | |||
| the data in S3 was more of a nicety, and I decided that checking the | |||
| data into a private git repo was adequate compared to the complexities | |||
| involved in configuring S3. git was a tried and tested way to store data | |||
| and restrict access while S3 for this usage was not, and hard to | |||
| configure. | |||
| After I wrote this blog post, a coworker linked me to the blog post titled | |||
| [Writing IAM Policies: How to Grant Access to an Amazon S3 Bucket](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/writing-iam-policies-how-to-grant-access-to-an-amazon-s3-bucket/). | |||
| It is concerning that this blog post has not been integrated, nor linked | |||
| to from any of the IAM or S3 documentation. This is a valuable resource | |||
| that should not be hidden. | |||
| I'm clearly not the only one that has had issues configuring S3 buckets. | |||
| The end of 2017 has shown a large number of organizations fail to | |||
| properly secure their S3 buckets, leaving many terabytes of data open | |||
| for public download. It is unacceptable that such a service is so | |||
| difficult to configure. The site https://s3stupidity.com/ lists the | |||
| large number of breaches, many of which are by large companies who | |||
| should have the technical chops (and $$) to properly configure it. | |||
| Security controls need to be simple and clear. Their descriptions need | |||
| to be accurate and concise in what they do, and how they do it. Amazon | |||
| does have a number of good resources, but they do not have a | |||
| comprehensive guide for what each permission does. You cannot blame | |||
| users for security failures when you make it next to impossible to | |||
| configure properly. | |||
| Edited to remove a couple extra words. | |||
+ 163
- 0
content/2018/07/making-freebsd-magnet-links.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,163 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: Making FreeBSD magnet links | |||
| description: > | |||
| Making FreeBSD magnet links | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2018-07-03' | |||
| time: 4:49 PM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - FreeBSD | |||
| - magnet | |||
| --- | |||
| For the last few years, I've been producing torrents and publishing | |||
| magnet links, but there is some special work that I do to make these. | |||
| The first few releases, I inserted a bogus tracker into the torrent, | |||
| because despite there being plenty of tools out there for producing | |||
| trackerless (DHT) torrents, they were all GUI and I never found any that | |||
| were command line based. The other was there was/is no tool for | |||
| extracting the info hash and building the magnet link. There may be | |||
| tools now, but I couldn't find any when I started 3 years ago. | |||
| The following steps are based upon the recent release of FreeBSD 11.2-R, | |||
| adjust as necessary. | |||
| 1. Fetch FreeBSD into a directory (I create a per release directory). There | |||
| are a few directories that you have mirror, I use wget for this. The | |||
| mirroring feature for wget isn't great. After each command I have to | |||
| remove the `CHECKSUM.SHA256`, `CHECKSUM.SHA512` and `index.html*` files. | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/ISO-IMAGES/11.2/ | |||
| $ wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/VM-IMAGES/11.2-RELEASE/aarch64/Latest/ | |||
| $ wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/VM-IMAGES/11.2-RELEASE/amd64/Latest/ | |||
| $ wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/VM-IMAGES/11.2-RELEASE/i386/Latest/ | |||
| ``` | |||
| 2. Fetch the signature files: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ wget https://www.freebsd.org/releases/11.2R/CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-{amd64,i386,powerpc,powerpc-powerpc64,sparc64,arm64-aarch64}.asc | |||
| $ wget https://www.freebsd.org/releases/11.2R/CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-{amd64,i386,arm64-aarch64}-vm.asc | |||
| $ wget https://www.freebsd.org/releases/11.2R/CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-arm-armv6-{BANANAPI,BEAGLEBONE,CUBIEBOARD,CUBIEBOARD2,CUBBOX-HUMMINGBOARD,GUMSTIX,PANDABOARD,RPI-B,RPI2,WANDBOARD}.asc | |||
| ``` | |||
| 3. Verify the GPG key that signed the above files. This is usually Glen | |||
| Barber's key, but not always. I have met and verified his fingerprint | |||
| in person, If you have verified someone's key who has signed Glen's | |||
| key, that is another good way. | |||
| 4. Verify the checksum files: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ for i in *.asc; do gpg --verify $i; done | |||
| You should see a bunch of lines like: | |||
| Warning: using insecure memory! | |||
| gpg: Signature made Fri Jun 22 09:33:50 2018 PDT | |||
| gpg: using RSA key 0x031458A5478FE293 | |||
| gpg: Good signature from "Glen Barber <gjb@FreeBSD.org>" [full] | |||
| gpg: aka "Glen Barber <glen.j.barber@gmail.com>" [full] | |||
| gpg: aka "Glen Barber <gjb@glenbarber.us>" [full] | |||
| gpg: aka "Glen Barber <gjb@keybase.io>" [unknown] | |||
| gpg: WARNING: not a detached signature; file 'CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-amd64-vm' was NOT verified! | |||
| ``` | |||
| The last line can be ignored. The non-`.asc` files were d/l'd and will | |||
| not be used. Make sure that all of the files report Good signature. | |||
| 5. In the past I have used BitTornado for other things, so I ended up | |||
| using it as the basis to make the tool for creating trackerless torrent | |||
| files. The modifications were simple. It appears that the original | |||
| BitTornado CVS tree is off-line (anyways, it was served insecurely), | |||
| but it looks like | |||
| [effigies/BitTornado](https://github.com/effigies/BitTornado) is | |||
| similar enough that it could be modified and used. I copied | |||
| `btmakemetafile.py` to `btmaketrackerless.py` and applied the following | |||
| patch: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ diff -u btmakemetafile.py btmaketrackerless.py | |||
| --- btmakemetafile.py 2004-05-24 12:54:52.000000000 -0700 | |||
| +++ btmaketrackerless.py 2016-10-10 17:13:32.742081000 -0700 | |||
| @@ -23,9 +23,9 @@ | |||
| def prog(amount): | |||
| print '%.1f%% complete\r' % (amount * 100), | |||
| -if len(argv) < 3: | |||
| +if len(argv) < 2: | |||
| a,b = split(argv[0]) | |||
| - print 'Usage: ' + b + ' <trackerurl> <file> [file...] [params...]' | |||
| + print 'Usage: ' + b + ' <file> [file...] [params...]' | |||
| print formatDefinitions(defaults, 80) | |||
| print_announcelist_details() | |||
| @@ -33,9 +33,9 @@ | |||
| exit(2) | |||
| try: | |||
| - config, args = parseargs(argv[1:], defaults, 2, None) | |||
| - for file in args[1:]: | |||
| - make_meta_file(file, args[0], config, progress = prog) | |||
| + config, args = parseargs(argv[1:], defaults, 1, None) | |||
| + for file in args[0:]: | |||
| + make_meta_file(file, None, config, progress = prog) | |||
| except ValueError, e: | |||
| print 'error: ' + str(e) | |||
| print 'run with no args for parameter explanations' | |||
| ``` | |||
| If you notice, the only thing that is done is to drop the first argument, | |||
| and instead of passing it into `make_meta_file`, a `None` is passed | |||
| instead. This will simply not add trackers to the torrent file. | |||
| 6. I then run the following script to verify the downloaded files, and | |||
| generate the torrent files: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ cat cmp.sh | |||
| #!/bin/sh - | |||
| # wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/ISO-IMAGES/11.2/ | |||
| # wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/VM-IMAGES/11.2-RELEASE/aarch64/Latest/ | |||
| # wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/VM-IMAGES/11.2-RELEASE/amd64/Latest/ | |||
| # wget -c -r -l 1 -nd --limit-rate=800k https://download.freebsd.org/ftp/releases/VM-IMAGES/11.2-RELEASE/i386/Latest/ | |||
| # wget https://www.freebsd.org/releases/11.2R/CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-{amd64,i386,powerpc,powerpc-powerpc64,sparc64,arm64-aarch64}.asc | |||
| # wget https://www.freebsd.org/releases/11.2R/CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-{amd64,i386,arm64-aarch64}-vm.asc | |||
| # wget https://www.freebsd.org/releases/11.2R/CHECKSUM.SHA512-FreeBSD-11.2-RELEASE-arm-armv6-{BANANAPI,BEAGLEBONE,CUBIEBOARD,CUBIEBOARD2,CUBBOX-HUMMINGBOARD,GUMSTIX,PANDABOARD,RPI-B,RPI2,WANDBOARD}.asc | |||
| grep -h '^SHA512' CHECK*.asc | sed -e 's/SHA512 (\(.*\)) = \(.*\)/\2 \1/' | sort -k 2 > sha512.from.asc | |||
| while read hash fname; do | |||
| if [ -e "$fname" ]; then | |||
| sigfile=`grep -l -- "$fname" *.asc | head -n 1` | |||
| echo checking "$fname", sig in: "$sigfile" | |||
| #res=`sha512 -q "$fname"` | |||
| res=`shasum -a 512 "$fname" | awk '{ print $1 }'` | |||
| echo "File is: $res" | |||
| if [ x"$res" != x"$hash" ]; then | |||
| echo missmatch! "$fname" | |||
| exit 1 | |||
| fi | |||
| if ! [ -e "$fname".torrent ]; then | |||
| btmaketrackerless.py "$fname" | |||
| fi | |||
| else | |||
| echo missing "$fname" | |||
| exit 1 | |||
| fi | |||
| done < sha512.from.asc | |||
| ``` | |||
| 7. Once all the torrents have been generated, I then make the magnet | |||
| links: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ cat btmakemagnet.sh | |||
| #!/bin/sh - | |||
| # metainfo file.: FreeBSD-10.3-RELEASE-sparc64-bootonly.iso.torrent | |||
| # info hash.....: 06091dabce1296d11d1758ffd071e7109a92934f | |||
| # file name.....: FreeBSD-10.3-RELEASE-sparc64-bootonly.iso | |||
| # file size.....: 203161600 (775 * 262144 + 0) | |||
| # announce url..: udp://tracker.openbittorrent.com:80 | |||
| # btshowmetainfo 20030621 - decode BitTorrent metainfo files | |||
| for i in *.torrent; do | |||
| btshowmetainfo.py "$i" | awk ' | |||
| $0 ~ "^info hash" { info = $3 } | |||
| $0 ~ "^file name" { name = $3 } | |||
| END { | |||
| print "magnet:?xt=urn:btih:" info "&dn=" name | |||
| }' | |||
| done | |||
| ``` | |||
| 8. I then create the magnet links file, and update the | |||
| [Torrents](https://wiki.freebsd.org/Torrents) wiki page. | |||
| Sorry about the code formatting. I don't know how to make it look better | |||
| in blogger. | |||
+ 118
- 0
content/2018/10/crash-dumps-do-i-submit-them.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,118 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: "Crash Dumps: Do I submit them?" | |||
| description: > | |||
| "Crash Dumps: Do I submit them?" | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2018-10-23' | |||
| time: 3:54 PM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - security | |||
| --- | |||
| TL;DR: No, do not submit your crash dumps. Consumers: No company has | |||
| sane crash dump policies to ensure your privacy and PII is protected, | |||
| minimized and secured. Companies: You need to ensure that crash dumps | |||
| are handled in a secure manner and that crash dumps are just that: a | |||
| crash dump. Anything not directly related to a crash dump should be | |||
| excluded. Usage statistics and the like do not belong in crash reports. | |||
| ## Why Not Send Dumps? | |||
| There is a long history of companies failing to minimize the data and | |||
| to protect it. Microsoft for years sent crash dumps over the internet | |||
| in the clear | |||
| ([WER & Privacy conerns](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_Error_Reporting#Privacy_concerns_and_use_by_the_NSA)). | |||
| This allowed the NSA to harvest them, and develop 0-days for issues that | |||
| MS failed to fix. Google's Chrome would send a screencap of the entire | |||
| Desktop along with it's crash dumps | |||
| ([link](https://twitter.com/vmjulix/status/857482886097715200)). It | |||
| previously would only send the window, but now sends the entire screen. | |||
| Though they provide a preview, there is no way to see exactly what | |||
| information will be sent. | |||
| I do not relish in advising people to not submit crash dumps as this | |||
| will impact developers ability to fix bugs. But as with all aspects of | |||
| security, companies continue to demonstrate that they are not willing | |||
| to do the work that is necessary to protect user's data and their | |||
| privacy. | |||
| ## Communication | |||
| You need to communicate to your users how crash dumps are handled. Just | |||
| saying, trust us, does not inspire confidence, as there are a large | |||
| number of cases of data breaches where the company has said exactly that | |||
| leading up to leaks. The policy is the first step to demonstrating that | |||
| you have thought about user's concerns and decided how you will handle | |||
| their personal and sensitive data. | |||
| The policy also helps shape how employees will treat the data too. By | |||
| having the policy, it is a reiteration to the employees that user data | |||
| isn't simply chaff, but that it needs to be protected and handled with | |||
| care. | |||
| Just saying that it's protected by a privacy policy isn't enough. For | |||
| example, Google Chrome's Report an Issue says that the information is | |||
| protected by their privacy policy, but if you read the Chrome browser | |||
| Privacy Policy, there is nothing in there that says how the data is | |||
| handled. That it is handled like the rest of the data collected does | |||
| not inspire confidence that the possibly confidential data that may be | |||
| included will be handled with greater care. | |||
| ## How to handle dumps | |||
| The first step is to ensure that what is collected in the dump has | |||
| minimum information needed to debug issues. Code paths (back traces) | |||
| are likely to be safe. Data, such as arguments to functions, may include | |||
| user data and needs to be carefully examined. There are many different | |||
| types of data that can be released from embarrassing (what website was | |||
| visited), to security breach (including cookies/tokens for web sites | |||
| that may not be yours), to confidential intellectual property leaking | |||
| (source code, designs, etc). Each of these may have different impact on | |||
| the user, but should never happen. | |||
| Second, crash dumps need to be transmitted confidentially. This means | |||
| either using TLS or encrypting the dumps with a tool like GPG before | |||
| sending. This ensures that unauthorized parties are unable to view the | |||
| contents. The NSA used the dumps to gather information for their | |||
| operations, which if Microsoft had properly protected their user's data, | |||
| this would not have happened. | |||
| Third, they need to be stored in a secure manner and able to be | |||
| expunged. It should even be possible for the user to remove the crash | |||
| dump if they discover that information was shared when it should not have | |||
| been. The life time that a company keeps the dumps should be limited. | |||
| If you haven't fixed a bug from five years ago, how do you know you can | |||
| reproduce it, or that if you are able to reproduce it, that the code is | |||
| still present in your current software? It the crash is a major issue, | |||
| it is likely that you'll have more recent dumps that exhibit the same | |||
| issue if it is a problem, so old dumps are just not as useful compared | |||
| to the data that may be present. | |||
| As crash data needs to be deleted, almost any cloud service is immediately | |||
| excluded unless other precautions are used, such as encryption. With | |||
| the cloud, you have zero visibility into how the data is managed and how | |||
| or when it is backed up. Cloud providers rarely tell you their retention | |||
| policies on back ups, and other policies that may keep data around. Do | |||
| they securely remove your VM's storage when they migrate it? Do they | |||
| ensure that storage is deleted from all clones, shards, servers and | |||
| backups when you delete it? If not, how long will that data stay around | |||
| before it is finally expunged. | |||
| Fourth, access to dumps need to be controlled. Auditing is a good first | |||
| step to know who is accessing the data, but additional measures like | |||
| limiting who has access needs to be used. Not everyone on the team needs | |||
| access to them. As they are classified, they can be assigned to teams | |||
| or people that need access to the data in them. This helps make sure | |||
| that an employee isn't trolling for nudes or other confidential | |||
| information. It should also limit how easy data is copied out of the | |||
| archive. How these controls are put in place will vary by company. | |||
| Edit: Case in point: I recently opened a support case with Apple. | |||
| Apple provides a program to collect data to send to them to help trouble | |||
| shoot the issue. The program collected 280 MB of data. When uploading | |||
| the data, Apple informs the user that it is their responsibility to NOT | |||
| submit any personal information that they don't want. There is no way | |||
| most people are qualified to look at the data, and even redact it | |||
| properly. I | |||
| [attempted to do so](https://twitter.com/encthenet/status/1057445997373087744), | |||
| and it took a very long time, and I'm not sure that I got everything. | |||
| Expecting a normal computer user to be able to do this is insane. | |||
+ 93
- 0
content/2018/10/tls-client-authentication-leaks-user.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,93 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: TLS Client Authentication Leaks User Info (pre-TLS1.3) | |||
| description: > | |||
| TLS Client Authentication Leaks User Info (pre-TLS1.3) | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2018-10-15' | |||
| time: 10:54 AM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - TLS | |||
| - security | |||
| --- | |||
| It's been long known that TLS is not the best privacy protecting | |||
| protocol in that SNI leaks what domain the client connects to. I'm a | |||
| bit surprised that I haven't seen the failure to protect user | |||
| information when using client authentication mentioned, but it's likely | |||
| that TLS client authentication is so rarely used, that this have not | |||
| been on anyone's radar. | |||
| TL;DR: Just don't use TLS client authentication on anything before TLS | |||
| 1.3. | |||
| With TLS 1.2 and earlier, if you use client authentication, the client | |||
| certificate is transmitted in the clear. This contains enough | |||
| information to uniquely identify the user. If it didn't, then there | |||
| would be no way for the server to do the authentication. | |||
| The danger of this is that Eve (eavesdroppers) on path will be able to | |||
| track your user's (or your) connections, where they connect from, figure | |||
| out how much data they transfer between to/from your site and likely | |||
| profile their usage. | |||
| I was confident that this was the case as I know that the entire | |||
| handshake is in the clear. It isn't till the Finished messages that | |||
| the session becomes encrypted. (TLS 1.3 fixed this by using a new | |||
| derived key, [sender]_handshake_traffic_secret, to encrypt all the | |||
| server params, which the client will use to encrypt it's response to | |||
| the certificate request in the server params.) I decided to verify | |||
| that this was the case. | |||
| I generated a server and a client certificate and key: | |||
| ``` | |||
| openssl req -batch -new -newkey rsa:1024 -days 365 -nodes -x509 -keyout server.key -out server.crt | |||
| openssl req -batch -new -newkey rsa:1024 -days 365 -nodes -x509 -keyout client.key -out client.crt | |||
| ``` | |||
| I then launched the server, and included the `-Verify` and `-CAfile` options | |||
| for `s_server` to request a client certificate: | |||
| ``` | |||
| openssl s_server -accept 5829 -cert server.crt -key server.key -Verify 5 -CAfile client.crt -debug | |||
| ``` | |||
| Then I ran tcpdump to capture the session: | |||
| ``` | |||
| sudo tcpdump -s 0 -n -i lo0 -w clientcert.tcpdump port 5829 | |||
| ``` | |||
| And then the client to connect to the server: | |||
| ``` | |||
| openssl s_client -connect localhost:5829 -key client.key -cert client.crt -debug | |||
| ``` | |||
| A usual, non-client authenticated connection and close was about 17 | |||
| packets, but when I included the client authentication, it became 42 | |||
| packets (the answer!). | |||
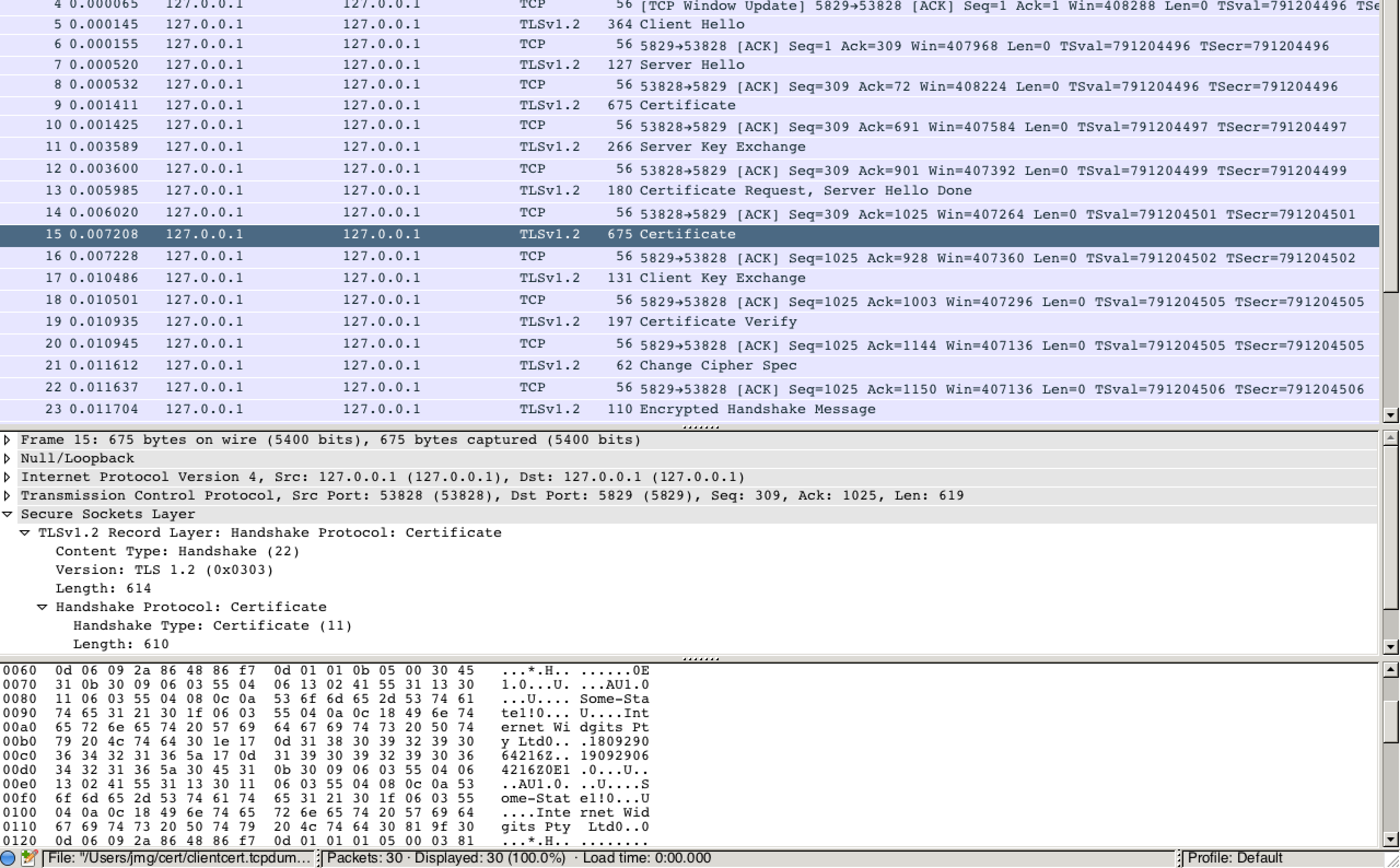
| I loaded the packet capture into wireshark, applied the SSL protocol | |||
| analysis and confirmed that the client certificate was present in clear | |||
| text: | |||
|  | |||
| So, there you have it. Do not use client authentication, pre-TLS 1.3, | |||
| if you care about the privacy of your users. | |||
| It is safe to use client authentication w/ a TLS 1.3 server as long as | |||
| the server requires all clients be 1.3 clients. If the key exchange | |||
| algorithm is one of DHE_DSA, DHE_RSA, or an ECDH key exchange algorithm, | |||
| the random bytes in the Hello messages are signed and these bytes are | |||
| used by TLS 1.3 for downgrade protection. As the signature covers these | |||
| bytes, the client would be able to detect any attempts to modify the | |||
| server or client handshake messages to force a downgrade before it would | |||
| send the client certificate. | |||
| Thanks to Mike Hamburg for reviewing an earlier version of this blog | |||
| post and pointing out that TLS 1.3 was not vulnerable to this and | |||
| helping w/ some of the research to prove it. | |||
| References: | |||
| * [TLS 1.2 Protocol Diagram](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5246#page-36) | |||
| * [TLS 1.2 ServerKeyExchange](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5246#page-52) | |||
| * [ECC Cipher Suites for TLS ServerKeyExchange Signature](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4492#page-20) | |||
| * [TLS 1.3 Protocol Diagram](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8446#section-2) | |||
| * [TLS 1.3 Server Hello](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8446#section-4.1.3) Downgrade Protection | |||
+ 3
- 0
content/2018/meta.yaml
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ | |||
| extends: blog.j2 | |||
| default_block: post | |||
| listable: true | |||
+ 106
- 0
content/2019/04/using-signal-on-server.html
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,106 @@ | |||
| --- | |||
| title: Using Signal on a server | |||
| description: > | |||
| Using Signal on a server | |||
| created: !!timestamp '2019-04-08' | |||
| time: 1:54 PM | |||
| tags: | |||
| - signal | |||
| --- | |||
| For a long while, I'd been using an email to SMS gateway to push | |||
| important notifications from my server, such as SMART error messages, | |||
| to my phone. After all the | |||
| [NSA warrantless surveillance](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NSA_warrantless_surveillance_(2001%E2%80%932007)), | |||
| I made a commitment to encrypt as much of my communications as possible. | |||
| When Signal came out, I adopted it because of it's strong encryption and | |||
| privacy. Ever since I've been wanting to use it for notifications from | |||
| my server. I finally got around to trying out the CLI version, and got | |||
| it to work. | |||
| The installation of the command line utility for Signal was more straight | |||
| forward than I was expecting. I decided to use | |||
| [signal-cli](https://github.com/AsamK/signal-cli) and I was a bit worried, | |||
| as it uses Java. Java has historically been difficult to run on FreeBSD | |||
| due to lack of support and draconian licensing terms. I was surprised | |||
| that the packages for OpenJDK 8 were both present and just worked on my | |||
| server. A simple `pkg install openjdk8` got Java up and running. | |||
| One thing to note is that the package said that fdesc and proc needed to | |||
| be mounted for Java to work, but I did not, and things still worked. | |||
| There are likely other parts of Java that may not work w/o those mounted, | |||
| but not for Signal. | |||
| As I have been using OSS for a long time, I like to build things from | |||
| source, so I followed the instructions at | |||
| [Building signal-cli](https://github.com/AsamK/signal-cli#building) and | |||
| got the command built with out any trouble. | |||
| Once the command was built, the | |||
| [Usage guide](https://github.com/AsamK/signal-cli#usage) provided the | |||
| basics, but didn't include instructions on how to verify the safety | |||
| numbers to ensure that the initial exchange was not MitM'd. There is a | |||
| [man page](https://github.com/AsamK/signal-cli/blob/master/man/signal-cli.1.adoc), | |||
| but it requires a2x and separate steps to build, but a little bit of | |||
| digging got me the necessary steps (also, it turns out that the adoc | |||
| format is a simple text format). | |||
| With a bit of searching, I found the `listIdentities` and `verify` | |||
| commands. There may have been another way, but because I had sent a | |||
| test message, my phone was listed: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ signal-cli -u +XXXXXXXXXXX listIdentities | |||
| +YYYYYYYYYYY: TRUSTED_UNVERIFIED Added: Sat Apr 06 18:43:15 PDT 2019 Fingerprint: ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ ZZ Safety Number: WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW | |||
| ``` | |||
| And then I needed to use the `trust` subcommand: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ signal-cli -u +XXXXXXXXXXX trust -v 'WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW WWWWW' +YYYYYYYYYYY | |||
| ``` | |||
| The hardest part of this was figuring out how to invoke the command upon | |||
| reception of an email. I used an alias listed in `/etc/aliases` to forward | |||
| the email to both the SMS gateway and myself. The issue with trying to | |||
| invoke the command from here was that the command was run as the `mailnull` | |||
| user, which of course didn't have access to my user's home directory to | |||
| read the private key. After a bit of debating, I remembered I use | |||
| `procmail`, and realized this was the best way to send the message. | |||
| I created a symlink for the command into my user's bin directory, created | |||
| a short script called `sendcell`: | |||
| ``` | |||
| $ cat ~/bin/sendcell | |||
| #!/bin/sh - | |||
| ~user/bin/signal-cli -u +XXXXXXXXXXX send +YYYYYYYYYYY | |||
| ``` | |||
| and then added a filter to my `.procmailrc` file. The filter at first | |||
| looked like this: | |||
| ``` | |||
| :0Wf | |||
| * ^TO_celluser@([^@\.]*\.)*example.com | |||
| | sendcell | |||
| ``` | |||
| But after the first test, it included all the headers, including all the | |||
| `Received` headers, so I updated it to use `formail` to remove all but the | |||
| `From`, `Subject` and `Date` (in case the message gets significantly delayed, | |||
| I can see by how much) headers: | |||
| ``` | |||
| :0c | |||
| * ^TO_celluser@([^@\.]*\.)*example.com | |||
| { | |||
| :0Wf | |||
| | formail -k -X From: -X Subject: -X Date: | |||
| :0 | |||
| | sendcell | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| and now I get the messages delivered to my phone securely! | |||
| It is tempting to use this to be able to invoke commands on my server | |||
| remotely, but there isn't much I need to do when I don't have my laptop | |||
| with me. | |||
+ 3
- 0
content/2019/meta.yaml
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ | |||
| extends: blog.j2 | |||
| default_block: post | |||
| listable: true | |||